To begin with, the omega fats are essential to your health and each provides different benefits. However, getting the proper amount of each in relation to the others is important as well. Thus, an imbalance of the various fats in your diet can be a problem for your health.
Fats in General
Before we get into the benefits of the various fats, let’s talk about their classification. To begin with, there are 3 main categories of fats known as saturated, unsaturated and trans-fats. All fats can be short, medium or long, but are classified according to the way in which it is bonded together chemically. Consequently, saturated fats are “saturated” with hydrogen molecules, like this:

Since they have a ‘straight line shape’ they fit together pretty tightly. Because of this, they have a high boiling point. As a result, foods high in saturated fat, like shortening are solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated fats are basically just like saturated fats but with one significant exception. Instead of being “saturated” with hydrogen, at least one bond between the fats is does not have as much hydrogen, but has a double carbon bond instead, like this:

This double bond makes the fat curl up more like a ball than a straight line. Thus, unsaturated fats cannot fit tightly together and therefore have a low boiling point. Hence, food high in unsaturated fats such as olive oil is liquid at room temperature.
Trans-fats are not found in nature but are entirely a product of chemically processed foods. They are just like unsaturated fats, but the double bond we talked about is chemically “backwards.” Of course, just because something is not “natural,” doesn’t make it “bad,” but in the case of trans-fat, no amount is helpful to your body.
Sub-Categories of Unsaturated Fats – The Omega Fats
Consequently, there are two main types of unsaturated fats, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated. In the event that it only has one double bond, it is mono-unsaturated. If it has more than one double bond it is polyunsaturated. And depending on where the bond is, it can be further classified as one of the omega fats; namely omega 3, 6, or 9. Specifically, the number just means how far the first double bond is from the end of the fat and has a significant effect on how it works in your body. Although there are a number of each type, here is an example of one of each:
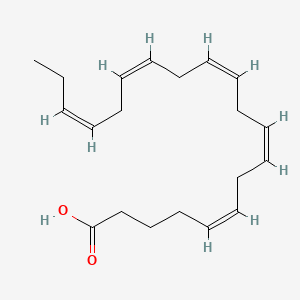
EPA, a type of omega-3
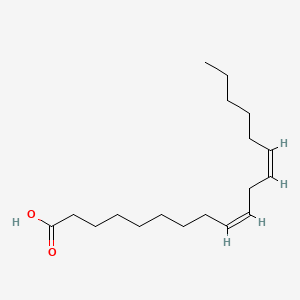
LA, a type of omega-6
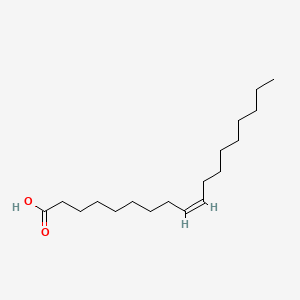
OA, a type of omega-9
Omega 3 Specifics

Omega-3’s are polyunsaturated, or have more than one double bond, and cannot be made by your body. In other words, you have to get them in your diet. Because of this they are often referred to as essential fats. And since they are so important to good health, the World Health Organization suggests eating oily fish at least twice every week1 as it provides three of the most common omega-3’s known as DHA, EPA and ALA.
- First is EPA, short for eicosapentaenoic acid, which happens to be a major player in the production of special molecules called eicosanoids. As it so happens, these chemicals are essential in the reduction of inflammation. Additionally, EPA is also known to reduce depression.2-3
- Second, DHA, or docosahexaenoic acid, looks a lot like EPA and constitutes about 8% of brain matter. This may not sound like much, but it is huge since proper brain development and function cannot happen without sufficient amounts of DHA.4
- ALA, also known as alpha-linoleic acid, is shorter than both EPA and DHA and can be converted to either. However, this process is not very efficient and most ALA is used by the body as an energy source.
All types of omega fats, especially 3’s, can be found throughout cell membranes of every type. In fact, without these omega fats, you wouldn’t have cell membranes and thus no life either. Thus, omega-3’s have significant roles in many aspects of your health.
Heart Health Benefits
Consequently, omega-3’s increase levels of HDL, the “good” cholesterol. This alone is a good enough reason to consume these omega fats, but they also decrease triglyceride (fat) levels in your blood, which can form plaques in your arteries.6-10 These plaques can and do lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Cognitive Function
Because omega-3’s are so important to the structure, and thus function, of brain cells, they reduce symptoms of depression, schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. As a matter of fact, even psychotic disorders can successfully be treated with these fats.11-15
Weight and Waist
Omega-3’s can even make you get skinnier. They can help you reduce your weight as well as your waist size.16-17
Liver Fat
Although you may not have heard of fatty liver disease, something tells me that you don’t want it. Fortunately, omega-3’s can help decrease the amount of fat in your liver.18-20
Baby Brain
As has been noted already, omega-3’s are great for the brain. Of course, this is especially true for babies who are developing a brain.4,21 Thus, building a brain without them is like building a house without any wood.
Inflammation
Given that pretty much every disease is associated with inflammation, controlling it is crucial. As you may already be aware, inflammation is when the body breaks down tissue. Luckily omega-3’s have natural anti-inflammatory properties to mitigate these damaging effects.22-24
Dementia
As a result of eating more fish, old people who do so have stronger brains. In fact, they tend to have improved memories, which is often a problem for older folks.25-26
Bone Health
You may be surprised at the fact that fat intake is significant to bone health. Nonetheless, people with higher omega-3 intake tend to experience higher bone mineral density.27-28
Asthma
Remember how we said that omega-3’s reduce inflammation? Ultimately asthmatic reactions are inherently inflammatory. Thus, these fats reduce the symptoms of asthma, particularly for young people.29-31
The typical Westernized diet is quite low in omega-3’s and thus dangerous to your health. If this is you, then you can expect to experience chronic disease such as obesity, diabetes and heart disease.32 Of course, none of these ends very well.
Omega 6 Specifics
 Omega-6’s are also polyunsaturated fats. But as explained previously, the first double bond is just 3 places down from an omega-3. These are also essential to your health and can only be obtained from your diet. Of the various types of omega-6’s, linoleic acid (LA) is the most common. Keep in mind, this is very similar, but NOT the same as ALPHA-linoleic acid (ALA) mentioned earlier. Nevertheless, LA once consumed can be converted to other fats such as arachidonic acid (ARA).33
Omega-6’s are also polyunsaturated fats. But as explained previously, the first double bond is just 3 places down from an omega-3. These are also essential to your health and can only be obtained from your diet. Of the various types of omega-6’s, linoleic acid (LA) is the most common. Keep in mind, this is very similar, but NOT the same as ALPHA-linoleic acid (ALA) mentioned earlier. Nevertheless, LA once consumed can be converted to other fats such as arachidonic acid (ARA).33
Like EPA and DHA, ARA also produces eicosanoids, but these ones tend to be PRO-inflammatory.34-35 While your immune system needs these eicosanoids to function properly, too many means inflammatory health issues like the ones mentioned already.36 The recommended ratio of omega-6’s to 3’s is 4:1 or less. But a typical Western diet is as much as 10 times this! For this reason, most of us need to change our omega fats by consuming more 3’s and fewer 6’s.37
Although they tend to be promote inflammation, some omega-6’s have displayed the tendency to fight disease. For example, gamma-linoleic acid (GLA) such as found in primrose and borage oils can be an excellent treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.38 One study even found that a certain drug for breast cancer was more effective when taken alongside GLA.39
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) is another common omega-6 found in dairy products, some plant oils and of course supplements. In fact, it is common among dieters and bodybuilders because of its ability to effectively reduce body fat. For instance, one study showed that just 3.2 grams per day in the supplemental form significantly reduced body fat.40
Omega-9’s
Unlike 3’s and 6’s, omega-9’s are monounsaturated, meaning they only have a single double bond in their chemical structure. But like the others, the “9” indicates where the double bond is found. The most common dietary form is called oleic acid. Some omega-9’s can be produced by your body, so they are not considered entirely essential. However, consuming them seems to have plenty of health benefits . For example, one particularly significant study showed a reduction in triglycerides by as much as 19% and VLDL’s (“bad” cholesterol) by 22% in diabetic patients.41 Others indicated an improved sensitivity to insulin as well as decreased inflammation.42
Common Dietary Sources of Omega Fats
- Omega-3
- Oily fish (best source)
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Anchovies
- Algal oils
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Flaxseeds
- Oily fish (best source)
- Omega-6
- Refined vegetable oils
- Soybean oil
- Corn oil
- Mayonnaise
- Nuts
- Walnuts
- Sunflower seeds
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Seeds
- Refined vegetable oils
- Omega-9’
- Vegetable and seed oils
- Olive oil
- Cashew oil
- Almond oil
- Avocado oil
- Peanut oil
- Nuts
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Walnuts
- Seeds
- Vegetable and seed oils
Supplements for Omega Fats
There are plenty of omega supplements on the market, many of which are a combination of omega fats 3,6 and 9. However, others are just omega-3’s and quite frankly these are usually the best option. As it has been suggested, most of us are lacking in the 3’s, not so much 6’s and 9’s. Thus, a fish oil supplement is an excellent choice for pretty much anybody.


